Overview¶
When using Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) you will at some point ask yourself: how does AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Kubernetes Role-based access control (RBAC) play together. Do they overlap? Are they complementary? What are the dependencies?
rbIAM aims to help you navigate this space.
If you want to learn more about the Why then read on here. For more background, peruse the terminology, and if you want to try it out yourself, check out the getting started guide now.
Motivation¶
For motivation, let's have a look at a concrete example, the Fluent Bit output plugin for Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose. In Centralized Container Logging with Fluent Bit we described the end-to-end setup and how to use it.
Zooming in on one path, the log shipping in EKS, it looks as follows:
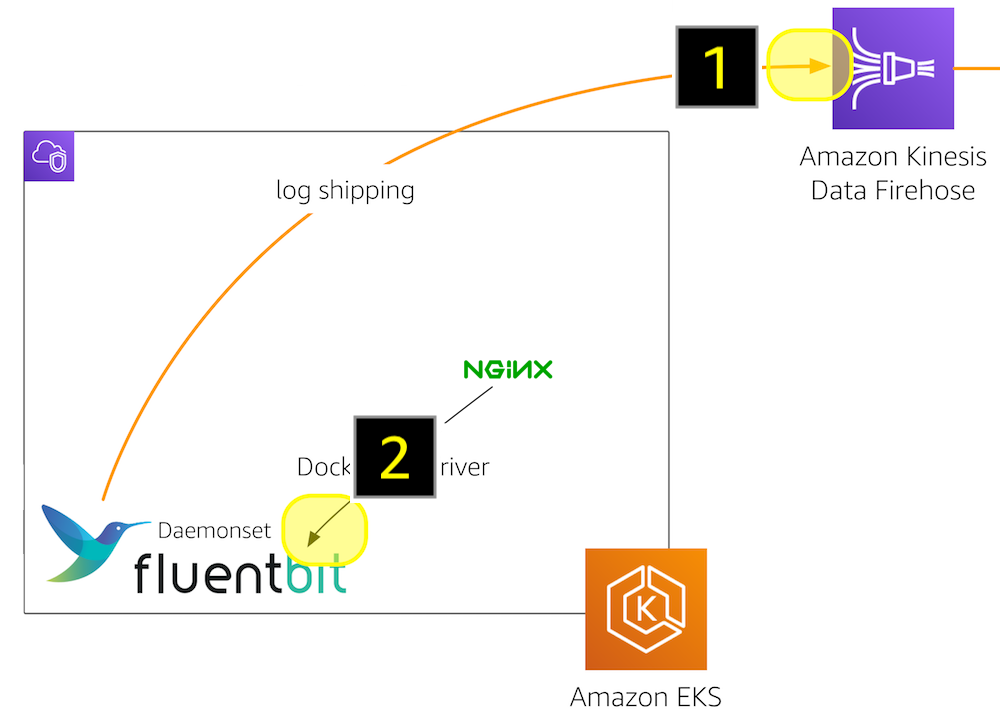
The Fluent Bit plugin is deployed as a daemon set and in order to do its job:
- It depends on an IAM policy, defined in eks-fluent-bit-daemonset-policy.json, giving it the permissions to write to the Kinesis Data Firehose, manage log streams in CloudWatch, etc., as well as
- It depends on a Kubernetes role, defined in eks-fluent-bit-daemonset-rbac.yaml, giving it the permissions to list and query pods, so that it can receive the logs from the NGINX containers.
Zooming in even further, focusing on the AWS and Kubernetes access control regimes in place, the relevant parts are:
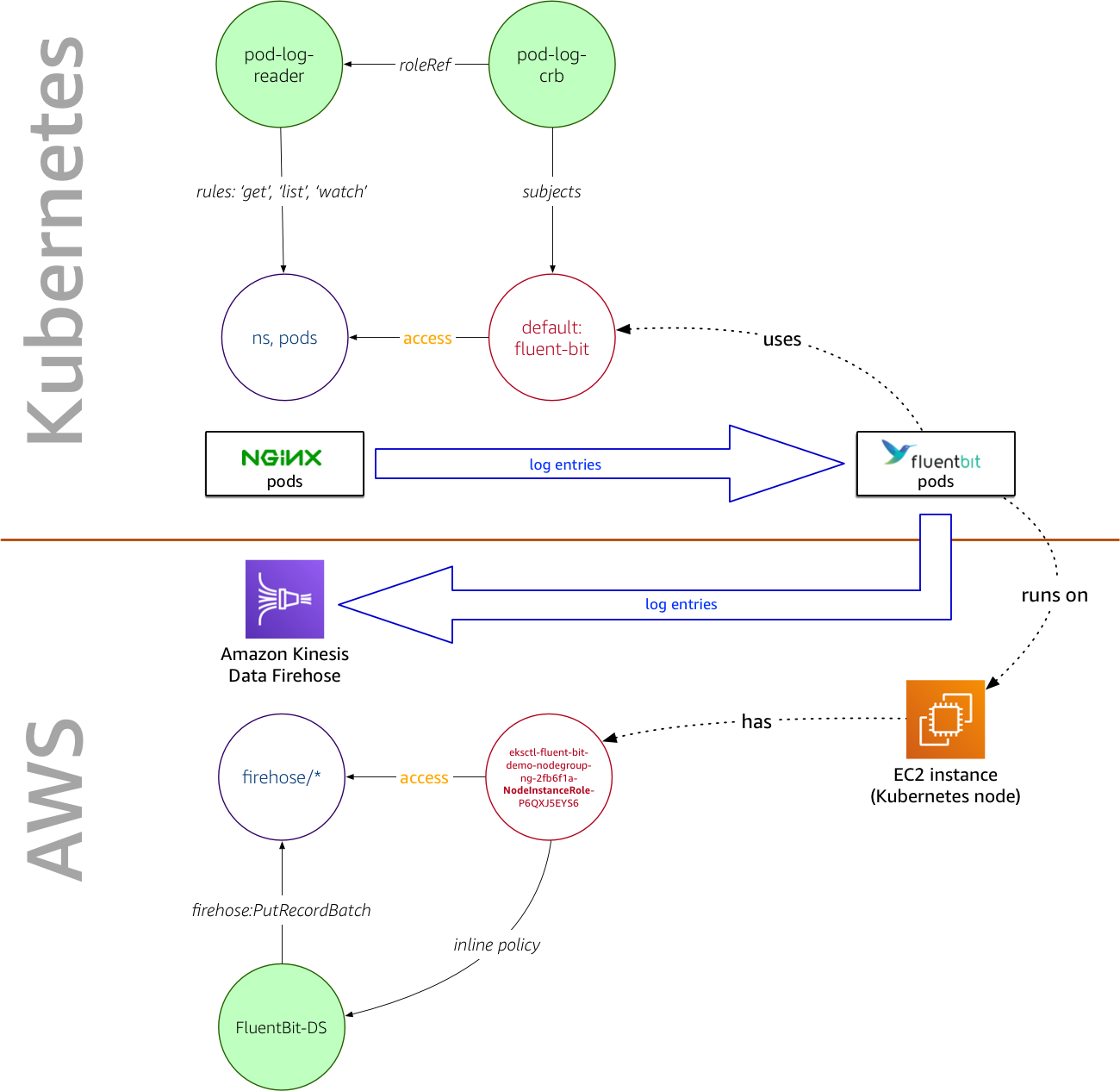
The Fluent Bit plugin has, through the Kubernetes RBAC settings in the pod-log-reader role, the permission to read the logs of the NGINX pods and, due to the fact that it is running on an EC2 instance with an AWS IAM role eksctl-fluent-bit-demo-nodegroup-ng-2fb6f1a-NodeInstanceRole-P6QXJ5EYS6 that has an inline policy attached, allowing it to write the log entries to a Kinesis Data Firehose delivery stream.
For a finer-grained description of the many moving parts here, have a look at the terminology section, which defines the terms and explains the motivational example in detail.
Use cases¶
You want to use rbIAM for:
- Exploring a given permissions setup, for example, an existing deployment in Kubernetes, when using EKS.
- Find the necessary permissions for a desired setup, both for the IAM policies and the RBAC roles.
- Understand how AWS services, such as S3 or CloudWatch or Firehose interact with Kubernetes resources, such as pods, from an access control perspective.
- Look up what a given Kubernetes resource can or can not do, concerning AWS services.
We expect that infra admins, devops roles, and also developers can
benefit from rbIAM. In order to use the tool, we assume you're familiar with
both AWS IAM and Kubernetes RBAC. If you want to brush up your knowledge, we
recommend first having a look at the terminology section.